Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) is nice and easy, if the entities you look at are of one of the typical levels of measurement (see below). But if one feature is a set, it becomes harder. In this post, I want to show a couple of possibilities.
Level of measurement
If you have features of this level of measurement.
| Scale | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative (categorical) | Quantitative (metric) | ||||
| Nominal- | Ordinal- | Intervall- | Ratio- | Absolute | |
| Empirical relations | Equivalence | Equivalence order |
Equivalence order emp. addition |
Equivalence order emp. addition emp. multipliation |
Equivalence order emp. addition emp. multipliation |
| Allowed transformationen | m' = f(m) f bijektive |
m' = f(m) f strictly monotonous |
m' = am+b with a>0 |
m' = am with a>0 |
m' = m |
| Examples of this scale | Telephone numbers, license plates, types, postal codes, gender | Grades, Degrees of hardness, wind force | Temp. in °C, °F, calendar time, geographic height | Mass, length, el. current | Number of particles, number of errors |
| Values of m | numbers, names, symbols | usually natural numbers | usually real numbers | usually real numbers > 0 | usually natural numbers |
Datasets
dblp
dblp is a bibliography website which contains publication data from almost 2 million publications.
Use DBLPParser to create a CSV file.
from collections import Counter
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import progressbar
import networkx as nx
from itertools import combinations
import clana.io
import clana.visualize_cm
# Load the data
df = pd.read_csv("articles.csv")
df["author"] = df["author"].str.split("::")
# Analyze the data
df = df[~df["author"].isna()]
authors = [author for authorset in df["author"].tolist() for author in authorset]
author_count = Counter(authors)
print("* Publications: {}".format(len(df)))
print("* Unique elements: {}".format(len(author_count)))
print("* Most common:")
most_common = sorted(author_count.items(), key=lambda n: n[1], reverse=True)
for name, count in most_common[:10]:
print(" {:>4}x {}".format(count, name))
unique_authors = sorted(list(author_count.keys()))
def get_biggest_clusters(edges, n=10):
G = nx.Graph()
for authorset in edges.tolist():
for author in authorset:
G.add_node(author)
for authorset in progressbar.progressbar(df["author"].tolist()[:10_000]):
for author1, author2 in combinations(authorset, 2):
G.add_edge(author1, author2)
print("Edges were added")
components = [c for c in sorted(nx.connected_components(G), key=len, reverse=True)]
return components[:n]
def create_matrix(nodes, edges):
n2i = dict([(node, i) for i, node in enumerate(sorted(nodes))])
# node to index
mat = np.zeros((len(nodes), len(nodes)), dtype=np.int32)
for edge in edges:
for a, b in combinations(edge, 2):
if a not in n2i or b not in n2i:
continue
mat[n2i[a]][n2i[b]] += 1
if a != b:
mat[n2i[b]][n2i[a]] += 1
return mat, sorted(nodes)
components = get_biggest_clusters(df["author"])
print("* Biggest clusters: {}".format([len(el) for el in components]))
component_w_publications = [(author, author_count[author]) for author in components[0]]
component_w_publications = sorted(
component_w_publications, key=lambda n: n[1], reverse=True
)
authors = [author for author, count in component_w_publications[:1_00]]
mat, labels = create_matrix(authors, df["author"].tolist())
clana.visualize_cm.main(
"coauthors.json",
perm_file="",
steps=1_000_000,
labels_file="labels.json",
zero_diagonal=False,
output="cm-ordered.pdf",
)
clana.io.write_cm("coauthors.json", mat)
clana.io.write_labels("labels.json", labels)
Results:
* Publications: 2,054,474
* Unique elements: 1,475,717
* Most common
1181x H. Vincent Poor
789x Lajos Hanzo
767x Witold Pedrycz
747x Mohamed-Slim Alouini
615x Chin-Chen Chang 0001
607x Dacheng Tao
591x Victor C. M. Leung
570x Wei Zhang
562x Wei Li
554x Wei Wang
* Biggest clusters (under first 10^6 publications): [761987, 52, 45, 44, 32, 31, 29, 28, 28, 28]
Then you can apply confusion matrix ordering to find authors who often work together (click on it to see large version):

The CMO technique is described in
Thoma, Martin. "Analysis and optimization of convolutional neural network architectures." arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.09725 (2017). Chapter 5.2.
MovieLens 20M
from collections import Counter
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import progressbar
import networkx as nx
from itertools import combinations
import clana.io
import clana.visualize_cm
# Load the data
df = pd.read_csv("movies.csv")
df["genres"] = df["genres"].str.split("|")
# Analyze the data
list_values = [value for valueset in df["genres"].tolist() for value in valueset]
value_count = Counter(list_values)
print("* Movies: {}".format(len(df)))
print("* Unique genres: {}".format(len(value_count)))
print("* Most common:")
most_common = sorted(value_count.items(), key=lambda n: n[1], reverse=True)
for name, count in most_common[:10]:
print(" {:>4}x {}".format(count, name))
unique_genres = sorted(list(value_count.keys()))
def get_biggest_clusters(edges, n=10):
G = nx.Graph()
for authorset in edges.tolist():
for author in authorset:
G.add_node(author)
for authorset in progressbar.progressbar(df["genres"].tolist()[:10_000]):
for author1, author2 in combinations(authorset, 2):
G.add_edge(author1, author2)
print("Edges were added")
components = [c for c in sorted(nx.connected_components(G), key=len, reverse=True)]
return components[:n]
def create_matrix(nodes, edges):
n2i = dict([(node, i) for i, node in enumerate(sorted(nodes))])
# node to index
mat = np.zeros((len(nodes), len(nodes)), dtype=np.int32)
for edge in edges:
for a, b in combinations(edge, 2):
if a not in n2i or b not in n2i:
continue
mat[n2i[a]][n2i[b]] += 1
if a != b:
mat[n2i[b]][n2i[a]] += 1
return mat, sorted(nodes)
components = get_biggest_clusters(df["genres"])
print("* Biggest clusters: {}".format([len(el) for el in components]))
component_w_publications = [(author, value_count[author]) for author in components[0]]
component_w_publications = sorted(
component_w_publications, key=lambda n: n[1], reverse=True
)
authors = [author for author, count in component_w_publications[:1_00]]
mat, labels = create_matrix(authors, df["genres"].tolist())
clana.io.write_cm("genre-combinations.json", mat)
clana.io.write_labels("labels.json", labels)
clana.visualize_cm.main(
"genre-combinations.json",
perm_file="",
steps=1_000_000,
labels_file="labels.json",
zero_diagonal=False,
output="cm-genre-combinations.pdf",
)
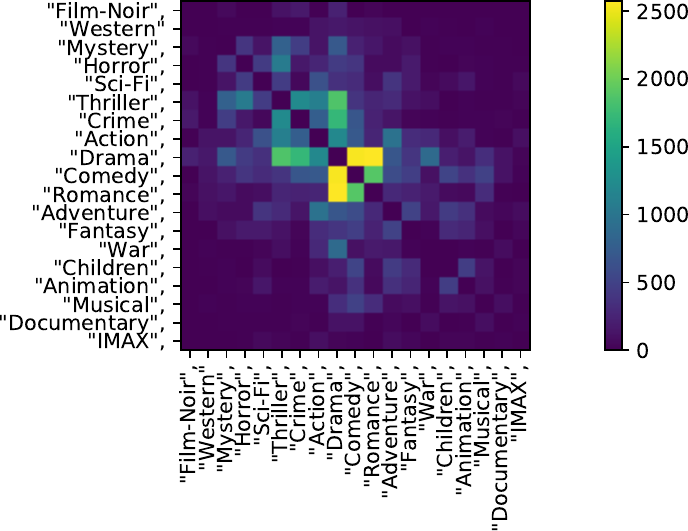
Results:
* Movies: 27278
* Unique genres: 20
* Most common:
13344x Drama
8374x Comedy
4178x Thriller
4127x Romance
3520x Action
2939x Crime
2611x Horror
2471x Documentary
2329x Adventure
1743x Sci-Fi
CMO: