Classification problems occur quite often and many different classification algorithms have been described and implemented. But what is the best algorithm for a given error function and dataset?
I read questions like "I have problem X. What is the best classifier?" quite often and my first impulse is always to write: Just try them!
I guess people asking this question might think that it is super difficult to do so. However, the sklearn tutorial contains a very nice example where many classifiers are compared (source).
This article gives you an overview over some classifiers:
- SVM
- k-nearest neighbors
- Random Forest
- AdaBoost Classifier
- Gradient Boosting
- Naive Bayes
- LDA
- QDA
- RBMs
- Logistic Regression
- RBM + Logistic Regression Classifier
Of course, neural networks are also one very powerful ML classifier I may not
forget. As sklearn does not have neural networks, I've installed
skflow.
Tutorial example
The sklearn tutorial creates three datasets with 100 points per dataset and 2 dimensions per point:
- Moons: Two interleaving half-circles
- Circles: A larger circle containing the smaller one
- Linear: A linearly seperable dataset
Each of those three datasets has added noise. This means for some points there might be no way of classifying them correclty.
Here are the results
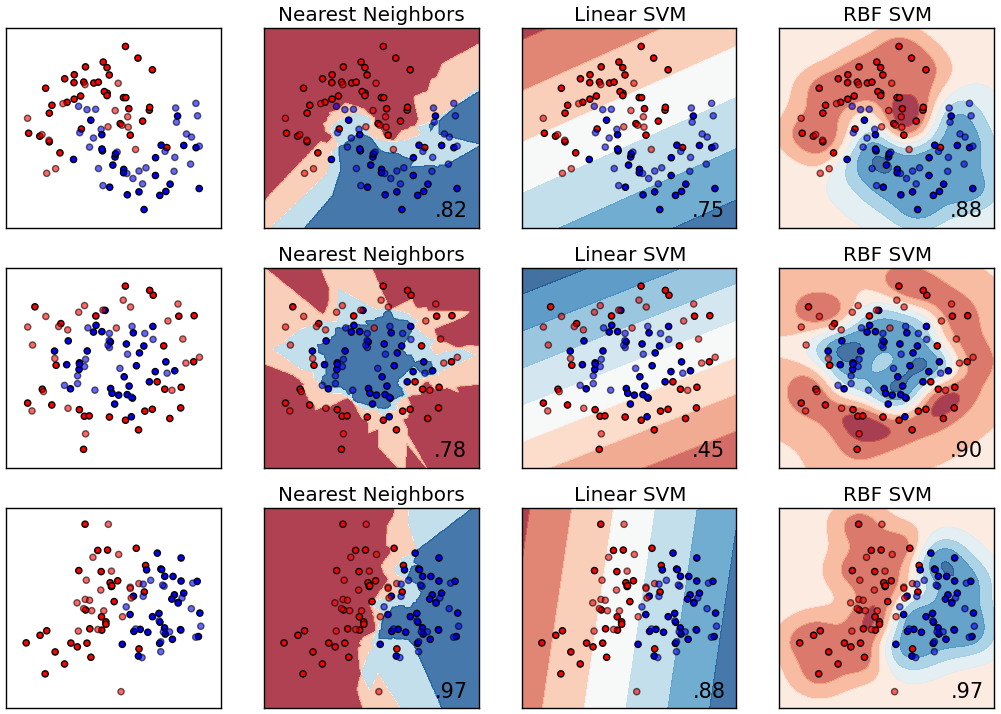
One can see that k nearest neighbors gives arbitrary decision boundaries. Overall, they look reasonable. However, there are often strange zig-zag patterns.
The linear SVM in contrast has a very easy decision boundary: a line. It is no suprise that it can't deal with the moons dataset. Note that a random guess would be right in 50% of the cases.
The RBF SVM has very nice decision boundary. It is smooth, matches the pattern and is able to adjust to all three examles.
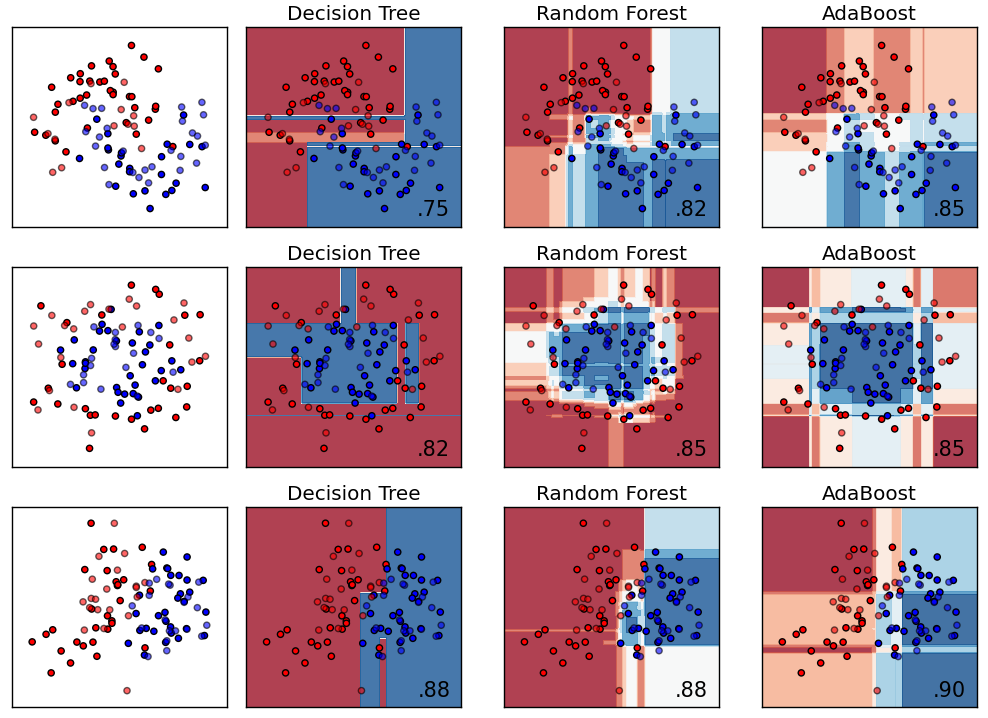
Decision Trees, Decision Forests and AdaBoost all show very similar patterns. The boundaries change in parallel to the coordinate axes which looks very unnatural.
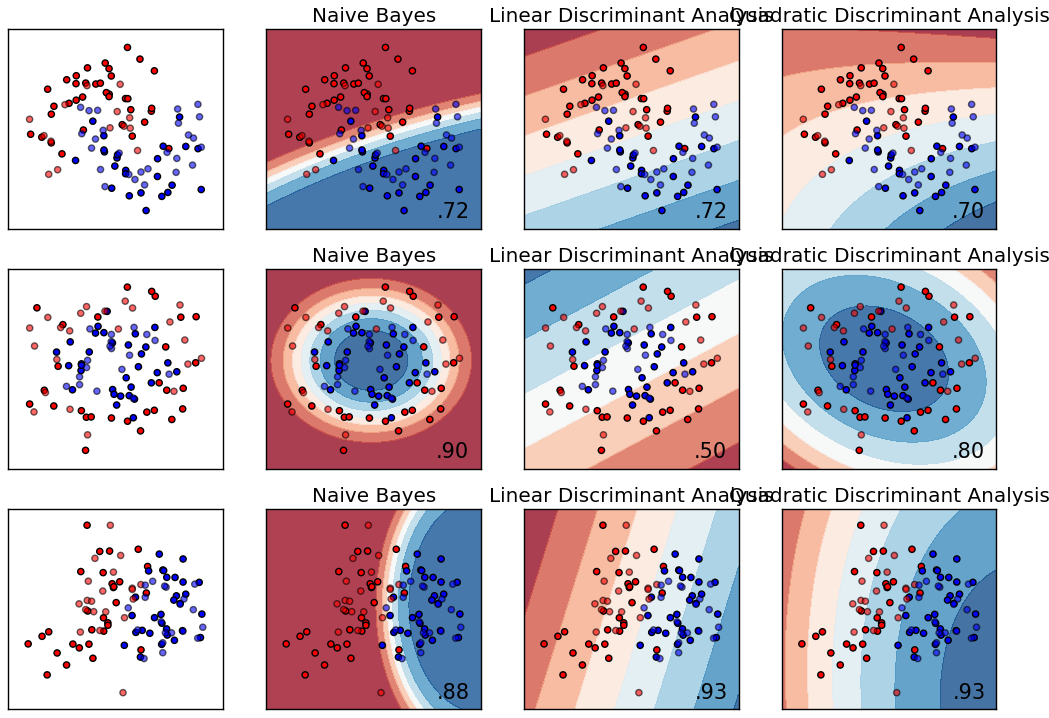
Naive Bayes shows nice, smooth patterns. However, those patterns seem to be a bit too simple. LDA is again linear (see linear SVM). Comparing QDA to Naive Bayes is interesting. Although they get similar performance for the first dataset, I would argue that the naive bayes classifier is much better as it is much more confident for its classification. Even more extrem is the last example. I'm astonished that the QDA gets 93% with that boundary; Naive Bayes seems to find a much better boundary.
The hardware
The following comparison is done on a PC with an Intel i7-4820K CPU and a NVIDIA GeForce GTX Titan Black GPU.
MNIST
MNIST is a dataset of \(28\text{px} \times 28\text{px}\) greyscale images. Each of the images contains a digit (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9). The task is to classify the image into one of the 10 digit classes.
Guessing randomly will give an accuracy of \(\frac{1}{10} = 0.1\).
Neural Networks
Please note that there are neural networks which get much better accuracy. Most notably the MNIST Expert tutorial with 99.2% accuracy.
Simple Network
Classifier: NN 500:200
Training time: 79.5696s
Testing time: 0.3480s
Confusion matrix:
[[2248 1 5 1 2 4 8 2 5 2]
[ 1 2565 10 1 1 0 2 7 1 0]
[ 7 2 2258 14 5 0 9 6 10 3]
[ 0 0 12 2294 0 23 0 6 3 10]
[ 0 3 3 0 2161 0 8 5 1 30]
[ 4 1 1 16 1 2014 17 1 5 9]
[ 11 7 1 0 5 6 2237 0 4 0]
[ 3 6 14 7 3 1 0 2355 10 18]
[ 3 7 3 14 2 17 4 1 2161 3]
[ 4 4 0 4 16 8 0 7 6 2340]]
Accuracy: 0.9798
Dropout Network
Classifier: NN 500:200 dropout
Training time: 118.2654s
Testing time: 0.3918s
Confusion matrix:
[[2250 1 7 1 1 1 5 4 4 4]
[ 1 2567 9 1 1 0 0 3 5 1]
[ 6 6 2272 3 2 1 3 10 8 3]
[ 0 0 26 2260 0 24 0 10 19 9]
[ 0 3 5 0 2152 0 7 3 1 40]
[ 8 3 3 12 2 1983 20 6 21 11]
[ 11 6 3 0 7 1 2237 0 6 0]
[ 2 7 13 3 11 0 1 2363 5 12]
[ 7 7 9 5 3 3 1 2 2170 8]
[ 3 3 1 3 13 2 0 19 8 2337]]
Accuracy: 0.9780
CNN
Classifier: CNN
Training time: 391.8810s
Testing time: 1.2035s
Confusion matrix:
[[2243 0 5 0 0 5 9 1 12 3]
[ 1 2548 20 4 2 0 1 6 6 0]
[ 3 8 2253 9 3 1 4 17 14 2]
[ 0 4 13 2290 0 12 0 9 11 9]
[ 2 4 5 0 2164 0 8 5 3 20]
[ 6 2 3 15 0 2016 9 3 9 6]
[ 12 12 1 1 6 6 2227 0 6 0]
[ 3 4 11 3 4 1 0 2374 4 13]
[ 3 15 6 13 4 11 3 8 2145 7]
[ 6 5 0 11 16 8 0 24 13 2306]]
Accuracy: 0.9769
SVM
There is a ton of literature / papers about SVMs. I've summed up the basics on Using SVMs with sklearn.
I've trained two SVMs: A simple, linear one and one with an RBF kernel as I found it online (I'm sorry, I don't remember where I found those parameters :-/).
Please note the the SVM implementation of sklearn does not use the GPU. However, there are GPU implmentations of SVMs around.
Linear SVM
Classifier: linear SVM
Training time: 168.6950s
Testing time: 158.0101s
Confusion matrix:
[[2226 0 9 2 6 12 8 3 11 1]
[ 1 2537 18 3 3 1 1 7 17 0]
[ 12 16 2158 25 24 6 27 19 25 2]
[ 3 7 46 2188 4 47 3 18 27 5]
[ 2 5 19 1 2117 1 8 6 3 49]
[ 18 13 11 73 20 1872 31 0 26 5]
[ 20 6 22 1 10 30 2179 0 3 0]
[ 5 10 32 11 30 5 0 2268 5 51]
[ 11 39 26 47 10 40 7 7 2018 10]
[ 11 9 9 24 64 8 0 61 14 2189]]
Accuracy: 0.9416
Adjusted SVM
Classifier: adj. SVM
Training time: 347.1539s
Testing time: 234.5724s
Confusion matrix:
[[2258 1 4 1 2 2 3 1 4 2]
[ 1 2566 9 1 1 0 0 7 3 0]
[ 4 1 2280 5 4 0 1 9 8 2]
[ 0 0 14 2304 1 13 0 6 8 2]
[ 2 2 2 0 2183 0 7 5 0 10]
[ 4 0 0 16 3 2026 12 1 4 3]
[ 7 5 3 0 5 2 2245 0 4 0]
[ 1 6 11 2 5 1 0 2373 5 13]
[ 3 9 4 9 4 10 2 3 2166 5]
[ 3 2 2 6 19 6 0 12 10 2329]]
Accuracy: 0.9840
Random Forest
Data:
n_estimators=50n_jobs=10
Classifier: Random Forest
Training time: 2.1359s
Testing time: 26.0763s
Confusion matrix:
[[2246 1 4 1 4 2 7 2 11 0]
[ 1 2543 18 5 5 2 3 7 4 0]
[ 7 2 2233 20 9 2 9 16 14 2]
[ 0 3 36 2240 0 20 3 16 19 11]
[ 3 1 5 0 2142 1 11 3 7 38]
[ 7 4 4 30 6 1977 16 3 14 8]
[ 13 11 4 0 10 15 2210 0 8 0]
[ 3 8 29 2 19 0 0 2315 7 34]
[ 3 12 18 17 9 26 4 7 2103 16]
[ 10 6 6 24 27 13 3 20 18 2262]]
Accuracy: 0.9641
Alternatively:
max_depth=5n_estimators=10max_features=1
Classifier: Random Forest 2
Training time: 0.2077s
Testing time: 22.2770s
Confusion matrix:
[[1955 32 63 64 12 4 109 21 13 5]
[ 1 2524 20 14 1 6 10 6 6 0]
[ 252 425 1198 151 64 1 145 15 55 8]
[ 136 195 140 1641 28 11 22 95 65 15]
[ 92 320 21 45 1199 9 76 153 8 288]
[ 312 383 67 655 78 268 47 94 134 31]
[ 199 364 125 58 96 13 1408 5 2 1]
[ 83 424 10 70 101 1 19 1555 56 98]
[ 392 574 44 147 52 17 71 106 773 39]
[ 71 338 11 43 579 2 8 632 24 681]]
Accuracy: 0.5715
k nearest neightbors
Classifier: k nn
Training time: 4.6439s
Testing time: 1261.7815s
Confusion matrix:
[[2260 1 4 0 0 1 6 2 2 2]
[ 0 2572 5 0 0 0 1 8 1 1]
[ 16 15 2235 9 1 0 5 26 5 2]
[ 2 5 14 2276 0 27 1 8 9 6]
[ 4 19 0 0 2131 0 8 4 0 45]
[ 10 5 3 28 5 1977 25 2 4 10]
[ 12 9 0 0 4 7 2239 0 0 0]
[ 1 18 4 1 12 0 0 2349 3 29]
[ 11 32 8 36 11 34 5 7 2053 18]
[ 6 8 4 14 26 4 0 19 5 2303]]
Accuracy: 0.9695
Decision Tree
Data:
max_depth=5
Classifier: Decision Tree
Training time: 3.1346s
Testing time: 0.0313s
Confusion matrix:
[[1767 0 11 25 12 120 137 71 114 21]
[ 1 2065 128 108 13 17 41 66 131 18]
[ 42 44 1248 37 121 21 227 76 339 159]
[ 33 22 32 1484 33 107 52 81 266 238]
[ 0 15 45 33 1284 42 42 45 213 492]
[ 42 10 21 229 166 577 137 123 254 510]
[ 34 33 66 24 103 65 1734 24 102 86]
[ 10 14 179 57 53 21 19 1775 79 210]
[ 1 98 129 43 43 42 160 29 1439 231]
[ 4 8 86 59 125 95 36 75 167 1734]]
Accuracy: 0.6540
Adaboost
You should note that you can use arbitrary base classifiers with Adaboost.
The default ones of sklearn.ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier is sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifies
Classifier: AdaBoost
Training time: 37.6443s
Testing time: 1.5815s
Confusion matrix:
[[1994 0 75 8 6 113 51 3 15 13]
[ 0 2435 27 22 2 10 12 37 42 1]
[ 97 39 1341 85 39 38 416 39 196 24]
[ 108 52 37 1508 13 313 66 64 122 65]
[ 11 16 48 23 1662 49 23 134 90 155]
[ 81 56 30 309 51 1255 57 17 129 84]
[ 29 28 151 7 80 43 1914 2 17 0]
[ 25 37 33 36 70 30 0 1761 37 388]
[ 30 80 48 215 16 85 30 19 1615 77]
[ 13 29 68 66 356 74 1 171 78 1533]]
Accuracy: 0.7367
Gradient Boosting
Gradient boosting with xgboost has won in the Rossmann Store Sales prediction
(source).
See also:
- Caterpillar Winners' Interview
- Caterpillar Winners' Interview: 3rd place
- Liberty Mutual Property Inspection, Winner's Interview
- Recruit Coupon Purchase Winner's Interview: 2nd place
- Dato Truly Native? Winner's Interview: 2nd place
Classifier: Gradient Boosting
Training time: 2409.8094s
Testing time: 0.4159s
Confusion matrix:
[[2214 1 3 5 10 8 9 3 24 1]
[ 1 2528 16 11 3 5 5 7 9 3]
[ 8 5 2165 34 16 5 12 22 37 10]
[ 1 9 27 2182 4 42 1 22 37 23]
[ 5 4 16 1 2088 5 12 5 10 65]
[ 9 6 7 41 8 1928 27 6 18 19]
[ 15 7 4 1 19 29 2181 1 14 0]
[ 6 16 27 15 22 6 0 2246 8 71]
[ 5 20 14 25 15 29 6 6 2057 38]
[ 6 10 8 24 49 15 1 54 17 2205]]
Accuracy: 0.9435
Naive Bayes
Classifier: Naive Bayes
Training time: 0.3814s
Testing time: 0.8863s
Confusion matrix:
[[2094 4 11 10 6 7 56 3 69 18]
[ 4 2432 9 11 2 4 28 1 77 20]
[ 278 64 703 143 6 4 558 4 528 26]
[ 202 136 18 791 5 5 106 21 886 178]
[ 96 26 16 14 296 8 169 13 535 1038]
[ 327 63 15 39 14 87 100 5 1253 166]
[ 34 51 17 1 1 5 2109 0 52 1]
[ 19 21 3 23 20 2 7 737 123 1462]
[ 39 326 13 16 8 18 25 7 1482 281]
[ 15 26 8 2 14 2 1 41 40 2240]]
Accuracy: 0.5615
LDA
Classifier: LDA
Training time: 20.6464s
Testing time: 0.0910s
Confusion matrix:
[[2131 2 10 14 12 47 20 4 36 2]
[ 0 2454 20 10 5 16 5 5 71 2]
[ 22 71 1873 77 51 8 82 20 101 9]
[ 5 32 56 1992 11 77 11 40 80 44]
[ 1 21 17 0 1983 12 12 2 21 142]
[ 19 18 11 112 18 1682 37 11 103 58]
[ 28 30 32 3 43 51 2046 0 37 1]
[ 16 57 25 20 70 8 0 1990 11 220]
[ 9 113 16 64 33 115 13 10 1781 61]
[ 15 10 6 35 133 14 0 122 22 2032]]
Accuracy: 0.8642
QDA
Classifier: QDA
Training time: 23.0527s
Testing time: 6.2259s
Confusion matrix:
[[2212 3 12 14 1 4 20 5 6 1]
[ 66 2409 12 10 0 0 32 2 39 18]
[ 961 25 689 143 3 1 310 2 166 14]
[1231 48 29 606 3 13 66 10 232 110]
[ 810 22 25 27 250 4 143 17 345 568]
[ 909 15 13 33 1 214 140 4 666 74]
[ 83 18 14 1 1 2 2146 0 6 0]
[ 81 13 6 52 14 2 1 776 120 1352]
[ 487 181 18 20 6 17 58 3 1320 105]
[ 65 14 12 7 10 0 0 23 33 2225]]
Accuracy: 0.5561
MNIST Summary
| Classifier | Accuracy | Training Time | Testing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLP (500:200) | 97.98% | 79.5696s | 0.3480s |
| Dropout NN (500:200) | 97.80% | 118.2654s | 0.3918s |
| CNN (32 5×5 filters : 2×2 max pool : 64 5×5 filters : 2×2 max pool : 1024) |
97.69% | 391.8810s | 1.2035s |
| Adjusted SVM | 98.40% | 347.1539s | 234.5724s |
| Linear SVM | 94.16% | 168.6950s | 158.0101s |
| Random Forest (n_estimators=50, n_jobs=10) | 96.41% | 2.1359s | 26.0763s |
| Random Forest (n_estimators=10, max_features=1, max_depth=5) | 57.15% | 0.2077s | 22.2770s |
| k nearest neightbors (k=3) | 96.95% | 4.6439s | 1261.7815s |
| Decision Tree(max_depth=5) | 65.40% | 3.1346s | 0.0313s |
| Adaboost | 73.67% | 37.6443s | 1.5815s |
| Naive Bayes | 56.15% | 0.3814s | 0.8863s |
| LDA | 86.42% | 20.6464s | 0.0910s |
| QDA | 55.61% | 23.0527s | 6.2259s |
| Gradient Boosting | 94.35% | 2409.8094s | 0.4159s |
| Logistic Regression (C=1) | 91.47% | 272.1309s | 0.0531s |
| Logistic Regression (C=10000) | 91.23% | 1807.0624s | 0.0529s |
IRIS summary
Just for fun, I tried the script from above with very minor adjustments to the IRIS flower dataset:
| Classifier | Accuracy | Training Time | Testing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBoost | 92.00% | 0.1203s | 0.0101s |
| Decision Tree | 92.00% | 0.0005s | 0.0001s |
| Gradient Boosting | 92.00% | 0.2227s | 0.0007s |
| LDA | 96.00% | 0.0027s | 0.0002s |
| NN 20:5 | 90.00% | 1.6628s | 0.0046s |
| Naive Bayes | 90.00% | 0.0010s | 0.0004s |
| QDA | 94.00% | 0.0009s | 0.0003s |
| Random Forest | 90.00% | 0.2147s | 0.1395s |
| Random Forest 2 | 90.00% | 0.1481s | 0.1249s |
| SVM, adj. | 90.00% | 0.0010s | 0.0004s |
| SVM, linear | 88.00% | 0.0006s | 0.0002s |
| k nn | 92.00% | 0.0007s | 0.0009s |
| Logistic Regression (C=1) | 88.00% | 0.0011s | 0.0001s |
| Logistic Regression (C=1000) | 92.00% | 0.0010s | 0.0002s |
| RBM 100 | 78.00% | 0.0233s | 0.0003s |
| RBM 100, n_iter=20 | 70.00% | 0.0427s | 0.0003s |
| RBM 200, n_iter=40, LR=0.01, Reg: C=1 | 88.00% | 0.2463s | 0.0005s |
| RBM 200, n_iter=40, LR=0.01, Reg: C=10000 | 90.00% | 0.2437s | 0.0005s |
| RBM 256 | 84.00% | 0.0424s | 0.0006s |
| RBM 512, n_iter=100 | 84.00% | 0.0723s | 0.0010s |
TL;DR
Neural networks take their time to train and a feeling for the topology, but their classification results are nice and the testing time is good as well.
Random Forests and SVMs are also a model a type of model one should think of. However, the standard implementation is very slow compared to neural networks.
sklearn.lda.LDA
might also be worth a try. The rest seems to be quite bad compared with those
classifiers.
The code which generated the examples from above is here.