I just wondered how fast some simple operations are (in Python). Like the lookup of an element in a dictionary. Here you have some, tested on my ThinkPad T460p (i7-6700HQ).
Arithmethic
I added/subtracted/multiplied/divided a thousand pairs of numbers to test the speed of basic arithmetic operations. I expected them to be FAST; essentially
Let's have a look at the adding function:
def add(numbers):
return [a + b for a, b in numbers]
The disassembled cPython Byte-Code looks like this:
>>> import dis
>>> dis.dis(add)
2 0 LOAD_CONST 1 (<code object <listcomp> at 0x7feabba81300, file "<stdin>", line 2>)
2 LOAD_CONST 2 ('add.<locals>.<listcomp>')
4 MAKE_FUNCTION 0
6 LOAD_FAST 0 (numbers)
8 GET_ITER
10 CALL_FUNCTION 1
12 RETURN_VALUE
So you can see that it does more than BINARY_ADD. Still, the basic arithmetic
operations are FAST. I think the tuple unpacking might actually have dominated
the time here.
Here are the results:
add : min: 177.3μs, mean: 200.3μs, max: 522.2μs
subtract : min: 168.4μs, mean: 190.9μs, max: 538.8μs
multiply : min: 165.4μs, mean: 199.7μs, max: 515.8μs
divide : min: 176.3μs, mean: 213.7μs, max: 518.9μs
2**int (0..20) : min: 546.4μs, mean: 597.5μs, max: 945.3μs
3**int (0..20) : min: 591.4μs, mean: 648.8μs, max: 1091.0μs <- BigInt
3.131**int (0..20) : min: 295.0μs, mean: 304.2μs, max: 602.3μs
2**float : min: 343.1μs, mean: 371.9μs, max: 769.7μs
3**float : min: 347.3μs, mean: 375.0μs, max: 748.9μs
3.131**float : min: 275.3μs, mean: 299.3μs, max: 586.4μs
add_vectors : min: 3.5μs, mean: 4.0μs, max: 34.8μs
subtract_vectors : min: 3.4μs, mean: 4.1μs, max: 28.5μs
multiply_vectors : min: 4.0μs, mean: 4.3μs, max: 30.7μs
divide_vectors : min: 17.2μs, mean: 18.2μs, max: 71.9μs
You can see how bad this measure is with something like
durations = np.array(timeit.repeat("4+500000", repeat=5000, number=1))
which gives
add : min: 0.08μs, mean: 0.15μs, max: 1.38μs
subtract : min: 0.08μs, mean: 0.15μs, max: 1.51μs
multiply : min: 0.06μs, mean: 0.14μs, max: 1.77μs
divide : min: 0.06μs, mean: 0.13μs, max: 1.36μs
modulo : min: 0.08μs, mean: 0.15μs, max: 1.59μs
I'm not sure if this test "suffers" from caching, especially as the max is way higher than the min and mean, but I guess it is save to say that all four basic arithmetic operations are about the same execution time and are less than 2μs. That would be about 5200 CPU cycles of my machine.
Element lookup
Timing how quickly one can retrieve the element from a direct access data structure by index. Not very surprisingly, lists are fastest. A bit surprising is that numpy arrays are quite a bit worse.
lookup(list) : min: 134.0μs, mean: 157.0μs, max: 482.0μs
lookup(dict) : min: 355.8μs, mean: 407.3μs, max: 1895.2μs
lookup(np array) : min: 711.1μs, mean: 855.7μs, max: 1665.5μs
Algorithms
Sorting
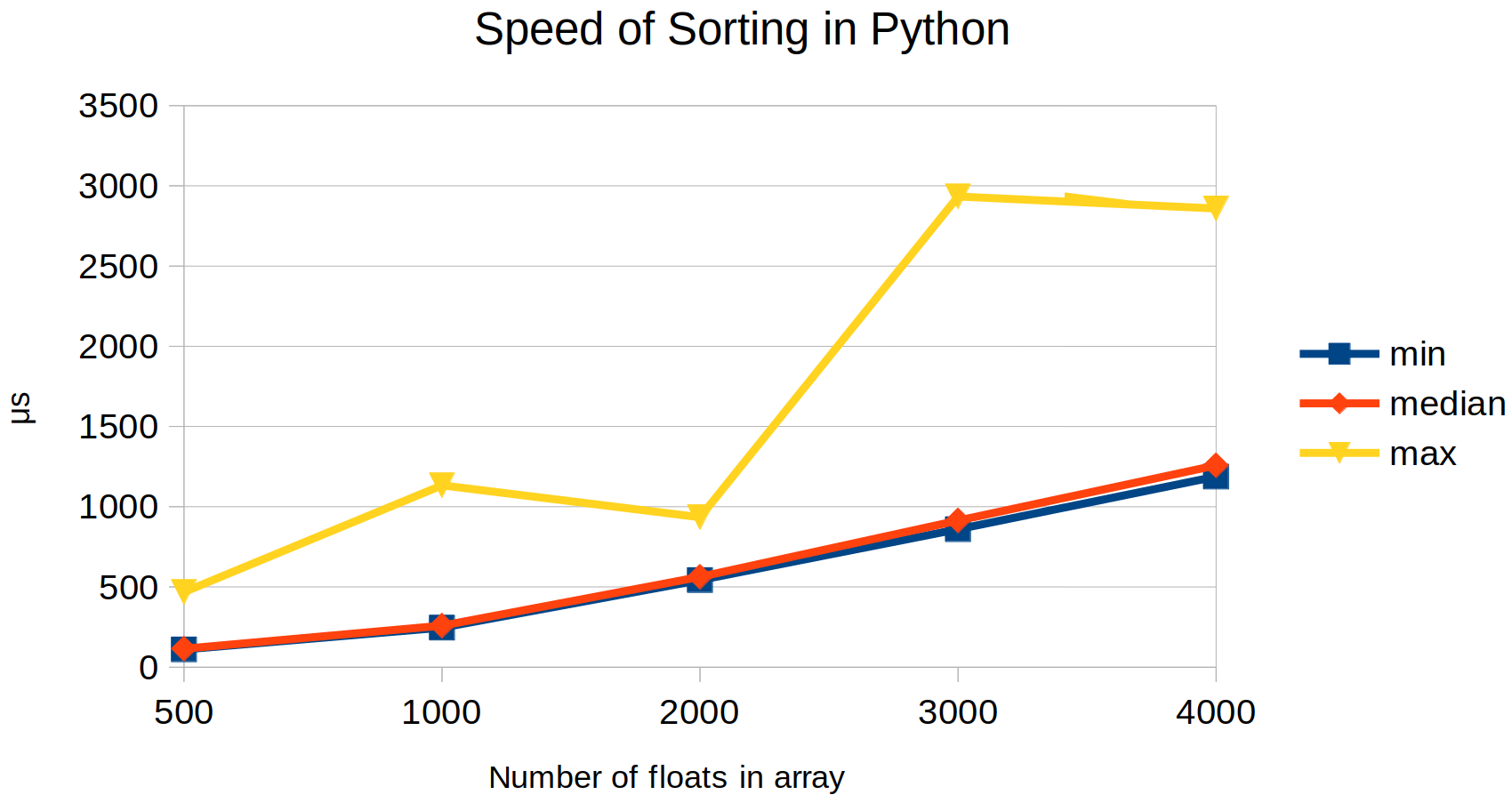
| Samples | min | median | max |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.6μs | 2.1μs | 191.7μs |
| 100 | 16.6μs | 24.9μs | 121.7μs |
| 500 | 110.6μs | 115.2μs | 467.9μs |
| 1000 | 246.1μs | 258.6μs | 1133.4μs |
| 2000 | 543.1μs | 562.6μs | 934.5μs |
| 3000 | 859.8μs | 913.8μs | 2933.8μs |
| 4000 | 1188.0μs | 1258.0μs | 2859.0μs |
| 5000 | 1519.6μs | 1631.4μs | 2828.4μs |
import timeit
import numpy as np
durations = np.array(
timeit.repeat(
"sorted(arr)",
setup="import numpy as np;arr = np.random.random(100_000)",
repeat=5000,
number=1,
)
)
print(
"min: {min:5.1f}μs, mean: {mean:5.1f}μs, max: {max:6.1f}μs".format(
min=min(durations) * 10 ** 6,
mean=np.mean(durations) * 10 ** 6,
max=max(durations) * 10 ** 6,
)
)
Networks
When you talk about "speed" in a network context, there are two important values:
- Latency
- Latency is measured in milli-seconds (ms) and answers the question: How long does it take for the first bit to be transmitted?
- Throughput (Bandwidth)
- Throughput is measured in kB/s and answers the question: If the first bit already arrived, how quickly will the rest be transfered?
Latency
Typical values:
- Accessing a CPU register: Less than 1ns!
- Accessing L1 / L2 CPU caches: 1ns - 10ns
- Accessing L3 CPU cache: 10ns - 100ns
- Ethernet Switch Latency: 50μs - 125μs
- Cable: Essentially non-existant as the signal travels with the speed of light
And some other corner stones:
- Ping (via WLAN) in average
- My router: 2.3ms
- joyn.de: 19.4ms
- twitter.com: 25.7ms
- google.de: 26.3ms
- wikipedia.org: 29.1ms
- martin-thoma.de: 29.4ms
- martin-thoma.com: 30.3ms
- netflix.com: 50.8ms
- write-math.com: 248.0ms
- Static pages with network:
- http://martin-thoma.de via hosting.de: 52ms - 61ms
- https://google.de: 110ms - 170ms
- https://joyn.de: 130ms - 190ms
- https://blog.fefe.de: 150ms - 180ms
- https://martin-thoma.com via GitHub: 320ms - 420ms
- https://netflix.com: 230ms - 500ms
- API request with network:
- https://write-math.com via namecheap; a symbol classification request: 550ms - 820ms
Throughput
And some throughput values (partially measured, partially looked up / calculated):
| Connection | Throughput | |
|---|---|---|
| Download | Upload | |
| Gigabit Ethernet | 1000 MBit/s | 1000 MBit/s |
| My Internet Connection | 285 MBit/s | 25 MBit/s |
| My Internet Connection (2020-04-12) | 96 MBit/s | 7 MBit/s |
| LTE (peak) | 37 MB/s | 9 MB/s |
| LTE (measured) | 14 MB/s | 2 MB/s |
| Audio Streaming (Low, 96kbps) | 0.012 MB/s | |
| Audio Streaming (Normal, 160kbps) | 0.020 MB/s | |
| Audio Streaming (High, 320kbps) | 0.040 MB/s | |
| Video Streaming (Low, 360) | 0.083 MB/s | |
| Video Streaming (Normal, 720p) | 0.250 MB/s (2.0 MBit/s) | |
| Video Streaming (High, 1080p) | 0.417 MB/s (3.3 MBit/s) | |
When you think about which internet contract to get, you might be wondering which speed is acceptable. The highest speed is probably necessary for video streaming:
| Speed | Comment |
|---|---|
| 0.5 Mbit/s | Minimum required for Netfix[1] |
| 1.5 Mbit/s | Recommended speed for Netflix[1] |
| 3.0 Mbit/s | Recommended speed for Netflix with standard resolution[1] |
| 5.0 Mbit/s | Recommended speed for Netflix with HD resolution[1] |
| 25.0 Mbit/s | Recommended speed for Netflix with Ultra-HD resolution[1] |
Combinations
Some measurements how quickly I get web pages:
get_webpage (martin-thoma.de, 2.3kB): min: 353ms, mean: 367ms, max: 390ms
get_webpage (google.de, 11.3kB): min: 532ms, mean: 548ms, max: 574ms
get_webpage (stackoverflow.com, 273.5kB): min: 1331ms, mean: 1686ms, max: 2462ms
See also
Code
See Github for the snippet.
Footnotes
-
Netflix: Internet Connection Speed Recommendations, read 2019-08-30. ↩